Learn how to use nslookup in Linux quickly and easily with this comprehensive guide! Get all the information you need for setting up and using this command.
What is nslookup command?
Nslookup (stands for “Name Server Lookup”) is a useful command for getting information from the DNS server also It is used as a network administration tool for querying the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain domain name or IP address mapping or any other specific DNS record. In this article, we will be showing how to use the Nslookup command to troubleshoot DNS-related issues.
Want to learn more about how DNS works and DNS records visit our previous tutorials.
Get to Know DNS: The Basics & How it Works
NSlookup acts as a tool to interact with DNS servers, allowing you to manually query them for information about domain names and IP addresses. It helps you understand the underlying DNS infrastructure and assists in troubleshooting DNS-related problems by providing direct access to DNS server functionality.
Installing nslookup on ubuntu
nslookup comes preinstalled on all major operating systems.
If nslookup is not installed you will be probably getting this error while trying to run the command “nslookup command not found“.
If you need to install it again on Ubuntu or another Linux distro featuring the APT package manager, install the dnsutils package:
sudo apt install dnsutilsOn CentOS, Fedora, and Red Hat, nslookup is part of the bind-utils package. Install it by running:
sudo dnf install bind-utilsVerifying our dns server.
Before using NSlookup, ensure that your computer’s DNS settings are correctly configured. Check the DNS server settings on your operating system or network configuration to ensure they are accurate. Incorrect DNS server settings can lead to inaccurate results.
In linux you can run the command
cat /etc/resolv.conf
Which will probably provide the values like 8.8.8.8 or 127.0.0.53 in the nameserver section.
If you get 8.8.8.8 it means that your system is configured to use Google’s DNS server.
If you get 127.0.0.53 it means that the DNS points to the local machine itself. That means your WIFI or ETHERNET connectivity.
Common use cases of nslookup command in Linux
There are many use cases of nslookup command in Linux. Here we are showing the very basic and commonly used use cases to query DNS records.
Let’s look the various options of nslookup command
View Domains IP address
This command is used to identify an IP address of a domain name. As we all know A record holds the IP address of the server where the domain is hosted nslookup will query the server and get the result back to us.
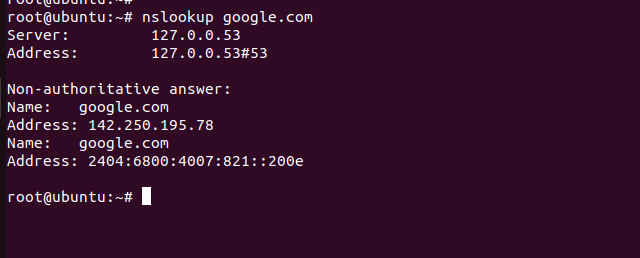
nslookup [domain.com]
Perform a reverse DNS lookup
This command is used to do the reverse DNS look-up by providing the IP Address as an argument to nslookup. usually, we query a domain name in order to get the IP address it is associated with but often in some cases, we need to understand IP address is related to a specific domain. For that purpose, we need a reverse DNS lookup.
root@ubundu:~# nslookup 142.250.71.46
46.71.250.142.in-addr.arpa name = maa03s35-in-f14.1e100.net.
View full details of a domain name
This command is used to get the details of all the DNS records of a particular domain name.
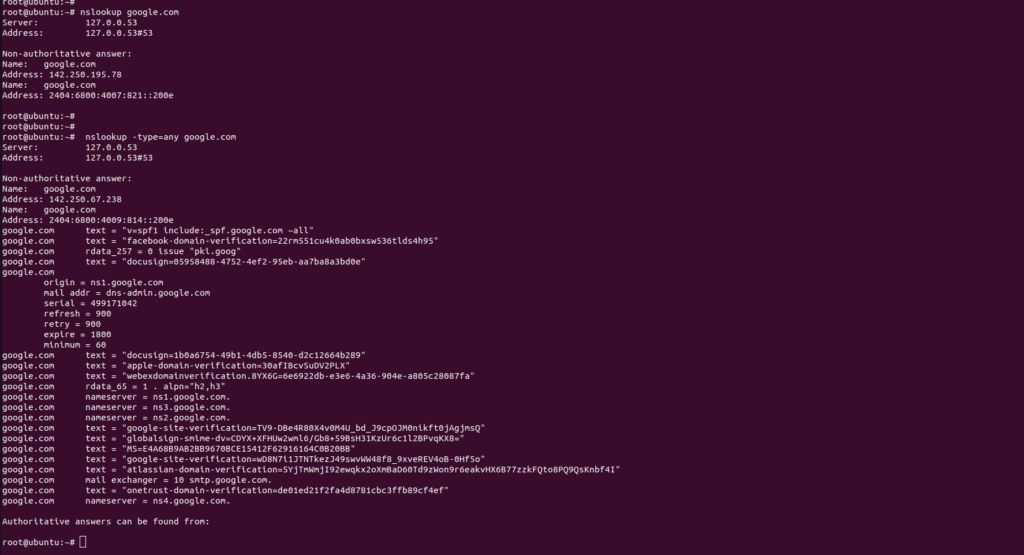
Syntax :nslookup -type=any domain.com
nslookup -type=any [domain.com]
View the MX record of a domain
MX records store all relevant Mail Exchange server data. This information is used to route all email requests for the domain to the appropriate mail server. This command is used to query the MX records of that particular domain.
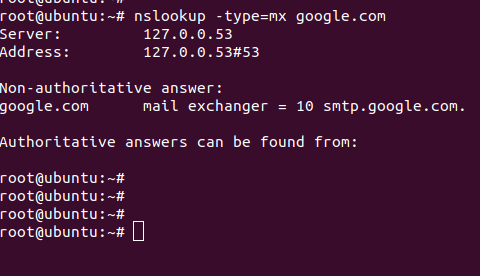
nslookup -type=mx domain.com
View Nameserver records of a domain
Nameserver is the server which holds all the records related to that domain name
To view the nameserver records of the domain name use nslookup command.
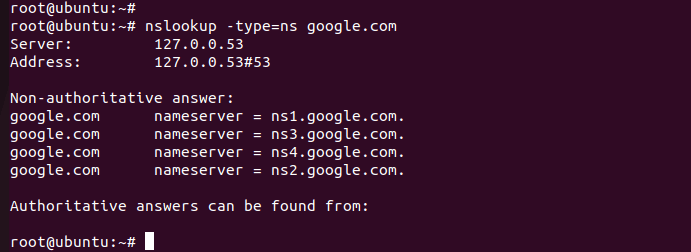
Similarly, you can query all the DNS records of a domain name by simply changing the record type in the above command
nslookup -type=mx domain.com (for example if you want to query the txt record type txt instead of mx).
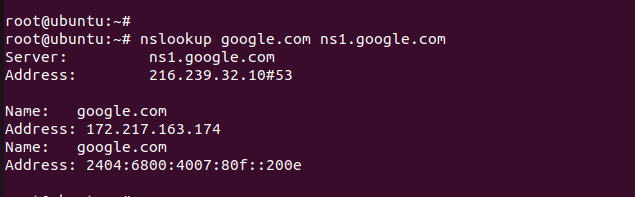
View information about a specific nameserver
nslookup domain.com [nameserver]
Here the output is limited to that specific nameserver. This is used to query the DNS records inside a specific nameserver.
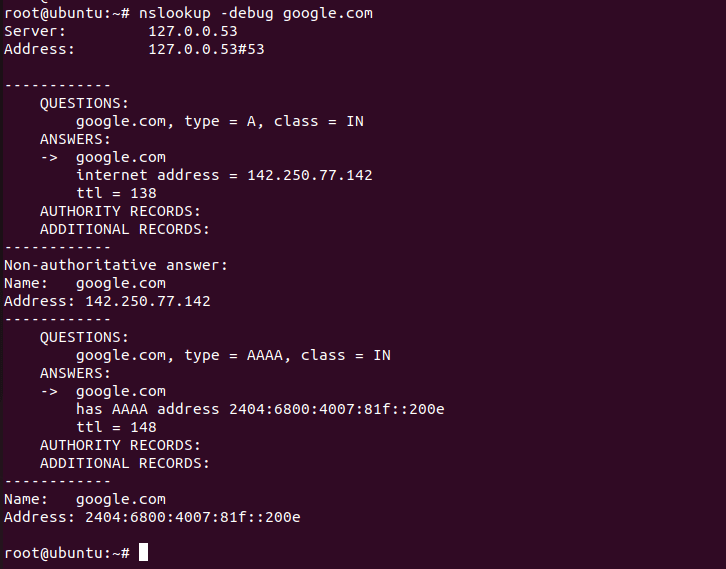
View debugging information
This command provides important and detailed information both for the question and for the received answer.
nslookup -debug [domain.com]
There are other tools available that offer similar functionalities. Here are a few alternative tools worth exploring:
Dig: Dig (Domain Information Groper) is a command-line tool available on most Unix-like systems. It provides detailed information about DNS records and performs DNS queries similar to NSlookup. Dig offers more advanced features and a flexible output format.
Online DNS Tools: Various online DNS lookup tools are available that offer web-based interfaces for performing DNS queries. These tools can be useful for quick DNS checks and troubleshooting from any device with internet access. Some popular online DNS tools include MXToolbox, DNSstuff, and UltraTools DNS Lookup.
Summary: In this blog, we have covered the basic use cases of nslookup command in Linux to troubleshoot DNS-related issues.
Visit official documentation for more details https://www.nslookup.io/